Facts on Breast Lift
| Medical term | Mastopexy |
|---|---|
| Who | women, especially after pregnancy or weight loss |
| Treatment | outpatient |
| Duration | 3-5 hours |
| Anaesthesia | sedation |
| After surgery | 6 weeks wearing a sports bra |
| Prices | from CHF 8'900: Breast lift |
A breast lift or mastopexy is usually requested by women who are suffering from physical and aesthetic restrictions caused by breasts that are too large or sagging. This can occur after breastfeeding or after pregnancy in general. Depending on the patient's disposition, the breast tissue can sag and cause problems such as skin irritation. During a breast lift, loose skin is removed, the breast is reshaped, raised and remoulded to the body.
Mastopexy
A breast lift (or mastopexy) can improve the size, shape and weight of the breast, making it possible for the patient to enjoy a more active lifestyle. After the operation, many women feel an easing of their everyday discomfort. The main objective of this operation is to achieve an aesthetic, but also functional, improvement.
The Breast Lift Procedure
The doctor selects the treatment method after careful consideration of the individual physical requirements of the patient being treated. He generally removes the skin around the nipple. The incisions are normally made in the natural contour of the breast and are largely hidden. In some cases an additional horizontal incision from the breast crease to the nipple is required. The doctor can then reshape the breast. There are a variety of techniques currently in use for a breast lift. The most frequently used method combines reshaping of the sagging tissue with moving the nipple to a higher position. The nipples can also be reduced in size at the same time.
If an implant is being used, the doctor places it either directly under the mammary gland or underneath the pectoral muscle. Experience has shown that this requires no additional incisions.
If required, the doctor will remove loose glandular tissue in the lower sections of the breasts before reshaping them.
After the doctor has marked the areas to be lifted and the new position for the nipple on the breast, the operating field is thoroughly disinfected and covered in a sterile dressing. Once this has occurred, the actual surgical procedure then follows, usually lasting from 1 to 2.5 hours. In order to prevent swelling in the wound area, a special bandage is applied, often shaped like a bra.
A breast lift procedure takes approximately 3 to 5 hours. The length of the operation depends on the extent of the clinical findings and the technique being used.
After the Mastopexy
A special bra must be worn to support the breasts. After the operation, the patient must be collected and driven home. She will also need some help around the house for the first few days after the operation. The small dressings are removed by the doctor after 14 days.
During the first months after surgery some women report sudden shooting pains in the nipples and in the side of the breast (like pinpricks). This pain is usually caused by reinnervation, which means that the skin nerves are starting to grow again, and the feeling improves with time. The ability to breastfeed usually remains after most operations, but this cannot be guaranteed.
Risks & side effects
- Internal bleeding in the skin, musculature and fatty tissue. This does not usually require treatment.
- Temporary irritation of the skin caused by disinfectant, dryness or touch. This usually subsides of its own accord.
- Swelling of the connective tissue or fatty tissue. This usually subsides if general anti-swelling measures are taken. A supplementary course of medication may be required.
- Secondary bleeding and haematoma may occur, even several days after the operation. For the most part, this requires no further treatment. An operation to stop the bleeding is only required in extreme cases.
- The edges of the wound may come apart under mechanical stress, e.g. when combing hair. This can have an undesirable effect on scar formation and in very rare cases can even require a scar correction procedure. Minor bleeding can cause necrosis (tissue death), which may require longer wound treatment or a follow-up operation.
- In very rare cases, local anaesthetic or the additional injection of haemostatic medication during anaesthesia can cause undesirable side effects such as allergic reactions, or reactions to the anaesthetic (swelling, itching, severe circulatory reactions and shock), additional side effects in the central nervous system (restlessness, cramp, respiratory disorders), an increase or decrease in blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmia and slowing of heartbeat.
- Scars: the operation cannot be performed without leaving scars. However, they are positioned in skin folds to ensure that they are as inconspicuous as possible and can be easily concealed. Small skin cysts may form in the scar area, but these can be treated quickly and easily.
- Problems during scar formation: depending on the constitution of the patient, bulging, painful scars that itch may occur (keloid scar tissue). Keloid scarring usually subsides through conservative treatment without the need for further operations.
- Excessive scarring of the skin and musculature really only occurs after years of nicotine misuse, or if there is severe internal bleeding with no inflammation. Scar deformations following complications such as these must often be improved with a follow-up procedure.
- Overcorrection: excessive correction can cause problems. In the first weeks after the operation, skin tension will improve on its own. An operation will be required to correct any continuing disorders.
- In some cases the cosmetic result may be unsatisfactory. This can be corrected with a further operation if necessary, or by removing the retaining straps.
- Wound healing may be impaired if smokers do not stop or significantly restrict their nicotine intake.
- Pigmentation changes in the skin, which can be permanent. Short-term or permanent loss of sensation can occur in the area around the breast or nipple.
Breast cancer
A breast lift procedure does not alter the risk of breast cancer as no glandular tissue is removed during the operation. The patient must continue to carry out her usual breast examinations.
Mommy Makeover
After pregnancy, a period of change begins. Many women look in the mirror and often feel restricted in their self-confidence after pregnancy. Pregnancy and breastfeeding have changed their body greatly. Often mothers complain about excess fat that has stored during pregnancy, about limp breasts and also a less taut abdomen.
With a healthy diet and a lot of exercise, most women try to tighten the abdomen after pregnancy, but often, unfortunately, this is not sufficient. In the prevention-center Zurich, we are here to help you to fulfill your wish of regaining your former body silhouette. With the so-called "mommy makeover", Dr. Köhler can treat the affected parts of the body and so, for example, lift the breasts.
According to your personal starting situation different surgeries (e.g. tummy tuck, breast lift and eyelid lift) are combined to shorten the recovery time of the "mommy makeover". Of course before the surgery, the medical conditions have to be checked.
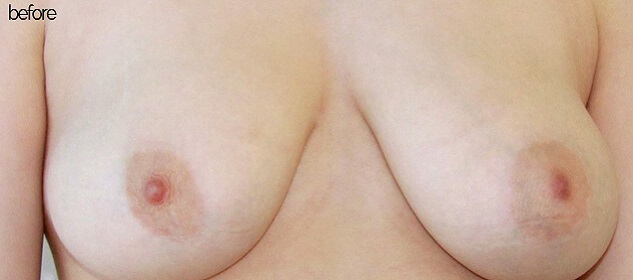
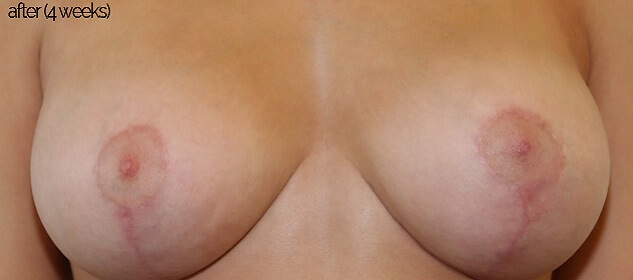
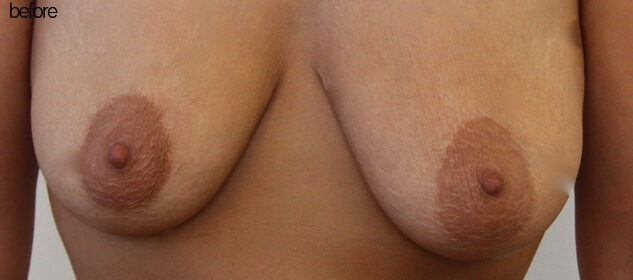
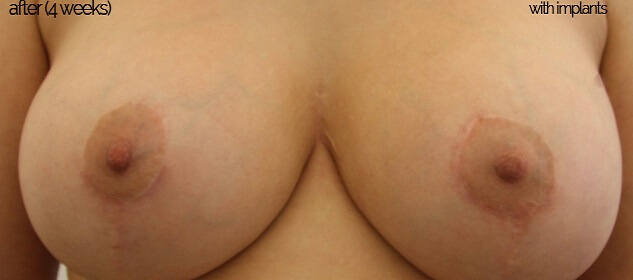
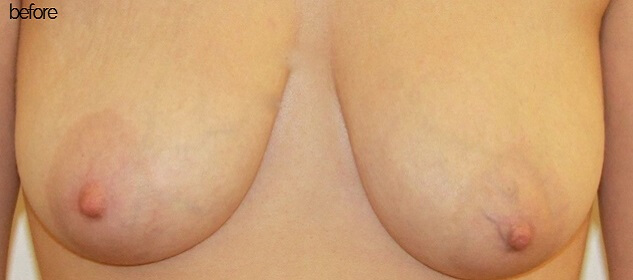
Before & After Pictures
Contact

PREVENTION-CENTER AG UTOSCHLOSS
Utoquai 31
8008 Zürich
How to get there
PREVENTION-CENTER AG ZUG
Aabachstrasse 8
6300 Zug
How to get there
PREVENTION-CENTER AG BERN
Kornhausplatz 7
3011 Bern
How to get there
PREVENTION-CENTER AG ST. GALLEN
Kornhausstrasse 25
9000 St. Gallen
How to get there
Coming Soon
VISITING HOURS
| MO - FR | 8 AM - 6 PM |
OVER THE PHONE
| MO - FR | 8 AM - 5 PM |